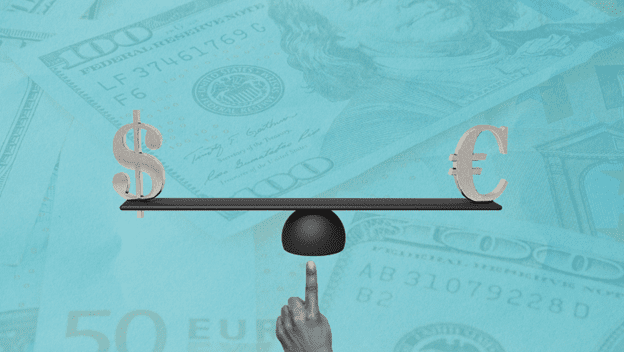
For the first time in two decades, the euro has crossed a major threshold: parity with the US dollar. The two currencies touched a 1-to-1 exchange rate after the euro briefly dipped below parity against the dollar on Wednesday, meaning that they now have the same worth.
Though the euro started the year on a strong note, it has taken a beating against the US dollar ever since the Russian-Ukrainian conflict in February, slumping as low as $0.9998 – down nearly 12% so far this year.
Here’s why the dollar-euro exchange rate has been dropping and what this means for the global economy.
Why is the Euro Falling Against the Dollar?
The 12% decline is down to multiple pressures, including supply chain disruptions, the energy crisis, and record inflation triggered by the Russian-Ukrainian conflict. For starters, Europe is at the epicenter of these geopolitical tensions and has suffered significantly as the region is heavily reliant on Russian oil and gas.
Surging energy and essential commodity prices, including gas, oil, wheat, and fertilizer, have pushed up global food and energy prices, driving inflation in Europe to a record 8.6% in June. Additionally, as Russia has been reducing natural gas exports to the European Union in retaliation for sanctions, gas rationing becoming a greater possibility as the risk of Russia cutting off gas exports increases. This turn of events has resulted in mounting recession fears in the Eurozone, and this has only dragged down the Euro even further.
Added to that, the U.S. Federal Reserve’s aggressive campaign to bring down inflation saw it raise the interest rate 3 times during 2022, which differs from the European Central Bank’s (ECB) actions, as it did not maintain interest rate hikes at a quick enough pace to accommodate this inflation. Coupled with an in-demand dollar, the falling Euro to USD exchange rate could also be attributed to the central banks moving at significantly different speeds in the United States and the Eurozone.
As the Fed raises interest rates, the rates on interest-bearing investments are likely to rise as well. So, as the Fed raises rates at a quicker pace than the ECB, higher interest returns will ultimately bring in investor money from euros into dollar-denominated investments. This means that those investors will have to sell their euros and purchase dollars to buy those holdings, driving the euro down and the dollar up.

What Does a Weaker Euro Mean?
A weaker Euro means different things for global businesses, consumers, investors, and banks. For businesses, fluctuating global currencies can create winners and losers depending on the region’s imports and exports. For example, American companies that have business in Europe will see their European revenue shrink if they choose to bring those earnings back to the U.S.
On the other hand, European businesses that sell their goods abroad might find that the weaker currency makes their exports more appealing, as the buyer’s currency is now more valuable. However, due to inflation, any imported goods or raw materials, especially oil, which is priced in dollars, will become more expensive.
This becomes a burden on the ECB, as the higher cost of imports adds to the region’s current inflationary pressures. The ECB is already under scrutiny and is set to raise interest rates, but higher rates can also stall economic growth, casting doubts as to whether the ECB will be able to tighten monetary policy aggressively enough to tame this inflation without exacerbating the economy.
For consumers, a sinking euro will add to the burden on European households already suffering from record-high inflation, as local prices increase. It will also become more expensive for Europeans and people who earn their wages in euros to travel abroad and spend in U.S. dollars. However, here in the UAE, a weaker euro could benefit consumers, as food items imported from the Eurozone get cheaper, leaving more disposable income in the hands of consumers.
What Pros And Cons Does a Stronger Dollar Present?
The stronger dollar is generally good news for US travelers considering a trip to Europe or buying goods abroad, since their dollar is worth much more, giving them more spending power.
As most commodities are priced in dollars, the strong dollar could lower the price of global commodities, easing inflation. But there may be a slower pace of global trade, as the main worry of a strengthening dollar is that it could hurt American exports abroad, as the foreign buyers’ purchasing power is weakened. This lower level of exports could, in turn, increase the current US trade deficit and reduce economic output.
At present, the US interest rate hikes have boosted the dollar’s appeal, and this 3% interest rate differential in favor of the US dollar is causing investors to park money in US dollar cash. Overall, the US currency remains a safe haven for investors across the globe, gaining strength by the day as investors navigate a shaky economic landscape in Europe by seeking the safety of the US dollar.

What is the EUR-USD Exchange Rate Impact on the UAE?
As the federal reserve maintains its more aggressive monetary policy the US dollar will only strengthen. As the UAE dirham (AED) is pegged to the US dollar, the UAE follows the same monetary policy as the United States, meaning the dirham will also strengthen.
Europeans, in particular, are benefiting from the currency’s decline against the dollar-pegged dirham by purchasing properties in Europe and frequently transferring money back home.
Moreover, the stable Dubai real estate market will create a hedge against other depreciating currencies and investors could certainly benefit from capital appreciation and a strengthening dirham. Consequently, we should see European investors seek stability in Dubai properties and move their funds to hedge against a deteriorating and volatile Euro.
There’s already strong demand for property in Dubai as it is, with many investors taking advantage of investor-friendly policies, flexible payment plans, and high potential ROI. With the euro expected to lose even more value, perhaps now is the time to take advantage of the economic uncertainty and invest in Dubai real estate.
Key Takeaway
There’s no denying that the past few years have been a challenging time for the global economy. Europe, in particular, has faced more challenges than most. The combination of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, soaring energy prices, and record high inflation has effectively hindered the continent’s post-pandemic recovery and, in turn, weakened the euro.
Now, it is expected that the European Central Bank will be raising interest rates more rapidly to curb the rise in inflation. Still, the U.S. economy is looking much more robust, meaning the Fed could continue tightening, further widening the interest rate gap.
And, as many businesses and consumers brace themselves for a recession in Europe, investors are now finding their safe haven in none other than the strengthened US dollar. Indeed, if you feel the Euro could drop further, naturally you’d want to park your money in a ‘safe haven’.
With the UAE dirham pegged to the US dollar, the Dubai real estate market is one such ‘safe haven’ experiencing unprecedented levels of demand, especially from European investors. The stable Dubai real estate market will help investors shield their wealth from the depreciating euro, as they also benefit from capital appreciation and the strengthening of the dirham.